
This is a motor issue, meaning it only affects a person’s ability to move.
#BRAIN STEM FUNCTION FULL#
This condition causes full paralysis of the body except for the eyes. One of the most severe effects that can occur after damage to the brain stem is locked-in syndrome. For example, patients who reach a minimally conscious state within three months have a high likelihood of regaining full consciousness compared to those who are still in a vegetative state after 12 months.

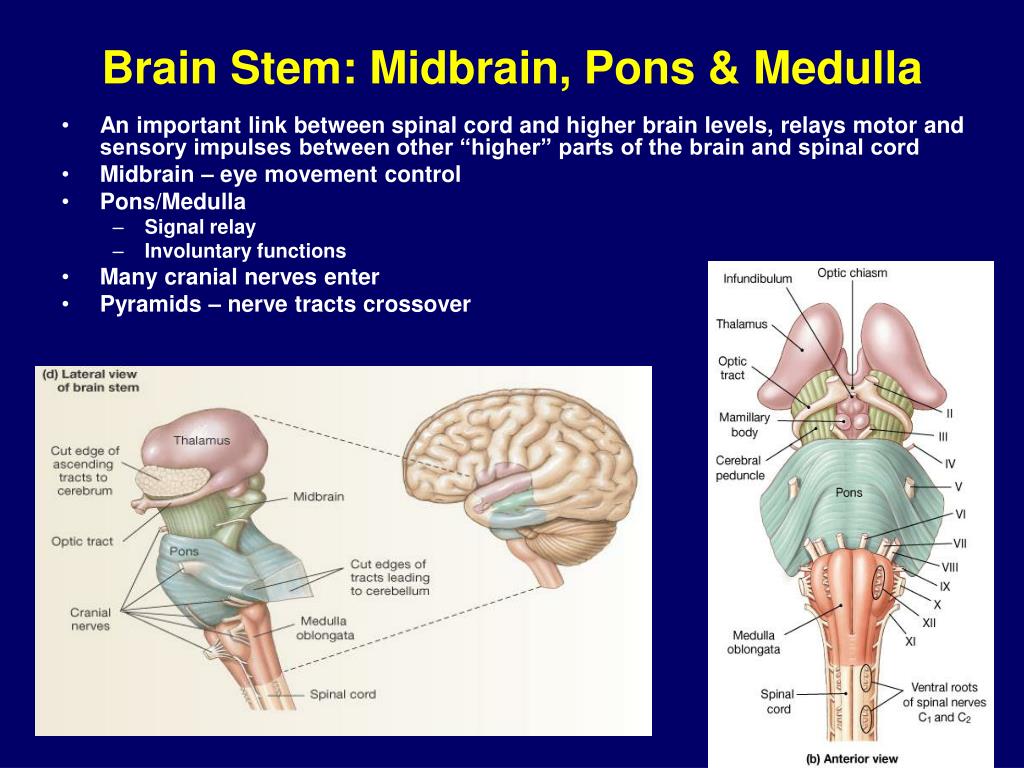
The faster the person progresses through these stages, the higher their chances of making a full recovery will be. Confusional state. Person is awake and aware but does not have full control over their behavior.Person can respond by blinking or smiling but falls in and out of consciousness. Vegetative state. Eyes may open and shut but the person cannot respond in a meaningful way, like squeezing your hand.After that, a person will usually pass through three stages of consciousness before finally becoming alert. Most comas after brain injury will last until the swelling goes down. When the brain stem sustains damage, the reticular activating system can be affected and result in a coma. The brain stem houses a network of neurons called the reticular activating system, which is responsible for states of consciousness and your ability to wake up. Here are some of the most common effects of brain stem damage: 1. Because every brain injury is different, brain stem injury survivors may experiences some, all, or none of the possible effects. Many of them affect basic life functions. Regardless of how brain stem damage occurs, there are various effects associated with this type of brain injury. You can also suffer brain stem damage after a brain stem stroke or diffuse axonal injury that tears the brain cells in the midbrain, pons, or medulla. Most injuries to the brain stem are the result of swelling in other areas of the brain as swelling forces the brain stem against the skull. Effects of Brain Stem Damageīrain stem damage is rare. The medulla oversees essential life functions, such as breathing, heart rate, and swallowing.īecause the brain stem is the link between the spinal cord and the rest of the brain, damage to the brain stem can also affect other functions besides the ones listed above. Medulla. Finally, at the bottom of the brain stem is the medulla.The pons acts as a bridge between the cerebellum and spinal cord and helps control your balance, among other things. Pons. Below the midbrain lies the pons.This structure plays a large role in muscle movement, particularly eye movement. Midbrain. At the top of the brain stem rests the midbrain.The brain stem is comprised of three distinct sections, which each section contributing to different functions: The brain stem is also responsible for critical functions that keep you alive and aware of your surroundings, making it one of the most important areas of the brain.

It connects the brain and spinal cord, which transports messages via neural pathways throughout the body.

The brain stem is located at the base of the skull directly above the spinal cord. Use the following links to jump ahead to certain sections: This article will cover everything you need to know about brain stem damage and how the recovery process works. Fortunately, it is often possible for a person with a brain stem injury to recover through rehabilitation. This is a collection of neurons, located in the upper brain stem, that projects to and stimulates the areas of the cortex that is responsible for awareness-the ability to think and perceive.When brain stem damage occurs, important basic life functions, like breathing, are impacted. The reticular activating system is the part of the brain stem that responsible for wakefulness. It is very important because it handles automatic functions like breathing, heart rate, and wakefulness. The brain stem begins underneath the brain and extends downward until it becomes part of the spinal cord. The thalamus plays a role in regulating awareness and emotional aspects of sensory experiences (For example: reaction to fear or hunger). This is the gateway for most of the sensory pathways. Additionally, there are deeper, inner structures of the cerebrum, such as the thalamus, a small structure located slightly above the brainstem. The cerebrum is made up an outer layer, called the cortex, which is responsible for thinking, learning, memory, and emotions. Obtaining a general understanding of the brain and its functions is important to understanding the rehabilitation process. There are three major parts of the brain: Learn About the Anatomy of the Brain and How Each Part Functions


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
